News
Solenoid Valves: A Comprehensive Guide to Selection, Operation, and Maintenance
Understanding Solenoid Valves and Their Applications
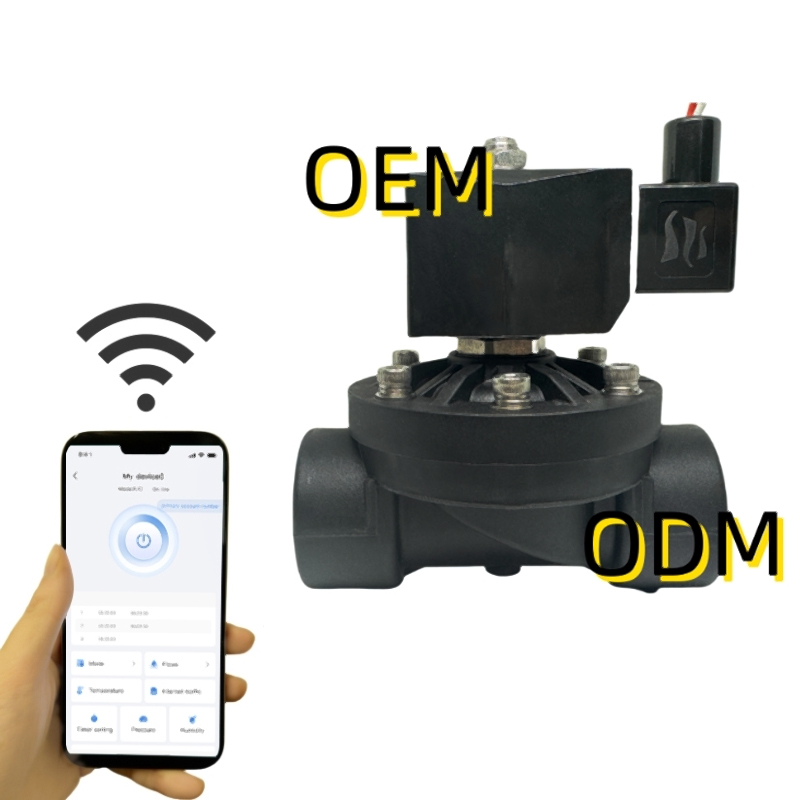
Solenoid valves are electromechanically operated valves widely used in fluid control systems across industrial, commercial, and residential applications. They provide precise control of liquid or gas flow through a pipeline by opening or closing in response to electrical signals. Their compact size, fast response time, and reliability make them ideal for automation, HVAC systems, irrigation, chemical processing, and more.
These valves can handle a variety of media, including water, air, steam, oil, and corrosive chemicals. Depending on their design, solenoid valves can operate in direct-acting, pilot-operated, or proportional modes, each suitable for specific pressure, flow, and automation requirements.
Types of Solenoid Valves
Selecting the right solenoid valve requires understanding the different types available. Here are the most common:
Direct-Acting Solenoid Valves
Direct-acting valves open or close directly using the solenoid's magnetic force. They are ideal for low-pressure systems or applications requiring precise flow control at small orifices. These valves are simple, reliable, and can operate without minimum pressure differential.
Pilot-Operated Solenoid Valves
Pilot-operated valves use system pressure to assist in opening the main valve, allowing them to handle higher flow rates and pressures efficiently. They are suitable for large pipelines and applications where minimizing solenoid coil size is essential.
Two-Way, Three-Way, and Four-Way Valves
The configuration of solenoid valves determines how fluid is directed:
- Two-way valves: Control flow in one inlet and one outlet, commonly used in on/off applications.
- Three-way valves: Can direct fluid from a single inlet to multiple outlets, often used in mixing or diverting systems.
- Four-way valves: Primarily used in pneumatic actuators for directional control.
Key Specifications to Consider
When choosing a solenoid valve, several technical specifications are crucial to ensure proper performance and longevity. The most important include:
Operating Pressure and Flow Rate
Check the valve’s rated pressure range to ensure it matches the system. Flow rate is determined by the orifice size and pressure drop across the valve. Selecting a valve with an adequate flow coefficient (Cv) ensures efficient system performance.
Voltage and Coil Type
Solenoid valves are available in AC and DC voltages. The coil must match the control system voltage, and considerations for duty cycle, ambient temperature, and power consumption are important for reliability and safety.
Material Compatibility
Valve body and seal materials should be compatible with the fluid being controlled. Common body materials include brass, stainless steel, and plastic. Seals are typically made of NBR, EPDM, FKM, or PTFE depending on chemical resistance and temperature requirements.
Installation Best Practices
Proper installation is critical for ensuring the reliable operation of solenoid valves. Key considerations include:
- Install the valve in the correct flow direction, as indicated by the arrow on the body.
- Ensure the electrical connection is correctly rated for voltage and properly insulated.
- Use clean, filtered media to prevent debris from obstructing the valve.
- Allow enough space around the valve for coil replacement and maintenance.
Troubleshooting Common Solenoid Valve Issues
Solenoid valves are generally reliable, but problems can arise due to electrical, mechanical, or media-related issues. Common problems and solutions include:
| Problem | Cause | Solution |
| Valve does not open | Coil not energized, clogged orifice, insufficient pressure | Check voltage, clean orifice, verify system pressure |
| Valve leaks | Worn seals, debris in seat | Replace seals, clean valve interior |
| Excessive noise | Water hammer, vibration, incorrect installation | Install dampers, check mounting, use appropriate valve size |
Maintenance Tips for Long-Term Performance
Regular maintenance ensures solenoid valves function efficiently and have a long service life. Practical tips include:
- Periodic cleaning of valve orifice and coil assembly to prevent build-up.
- Inspecting seals and diaphragms for wear or chemical damage.
- Testing coil resistance and voltage to ensure proper electrical operation.
- Replacing components proactively in high-cycle or critical applications.
Selecting the Right Supplier and Model
Choosing the right solenoid valve supplier is as important as selecting the correct model. Look for manufacturers who provide:
- Detailed datasheets with performance curves and material specifications.
- Technical support for installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance.
- Compliance with relevant industry standards, such as ISO, CE, or UL.
- Availability of replacement parts and accessories.
By combining correct selection, installation, and maintenance practices, solenoid valves can reliably control fluid systems across a wide range of industrial and commercial applications.



 English
English Español
Español