Industry knowledge
Smart climate management demands control actions that respond to both short-term fluctuations and slow seasonal trends. App Humidity Control Solenoid Valves excel when humidity sensing is combined with trend-aware algorithms: the app collects time-series humidity and uses moving-window statistics to distinguish transient spikes from sustained deviations, allowing the valve controller to avoid unnecessary cycling while maintaining target ranges.
Sensor strategy and placement for reliable humidity control
Sensor accuracy and location determine control quality. Place primary humidity sensors in representative air streams rather than near moisture sources or direct sunlight. For greenhouse canopies, a height-stratified sensor array helps detect microclimates; in HVAC ductwork, use a flow-conditioned probe to avoid readings skewed by recirculation. For redundancy, a secondary sensor can be used to validate readings and trigger maintenance alerts when divergence exceeds a configurable threshold.
Control logic: hysteresis, schedules and adaptive setpoints
Effective humidity control balances responsiveness with equipment longevity. Implement controlled hysteresis to prevent rapid open/close cycles: define a deadband around the setpoint and use minimum on/off durations. Combine schedule-driven setpoints from the app (day/night or crop-stage profiles) with adaptive setpoints that shift slowly based on external weather forecasts or soil moisture inputs to reduce water consumption and energy use.
Practical configuration recommendations
- Set a conservative deadband (e.g., ±3% RH) for rapid systems, tighten it where fine control is critical (e.g., tissue-culture rooms).
- Use minimum valve-on durations to prevent short cycling, matching actuation time to valve flow characteristics.
- Layer app schedules with local overrides so on-site systems can retain safety setpoints if connectivity is lost.
Communication stacks and app features that increase uptime
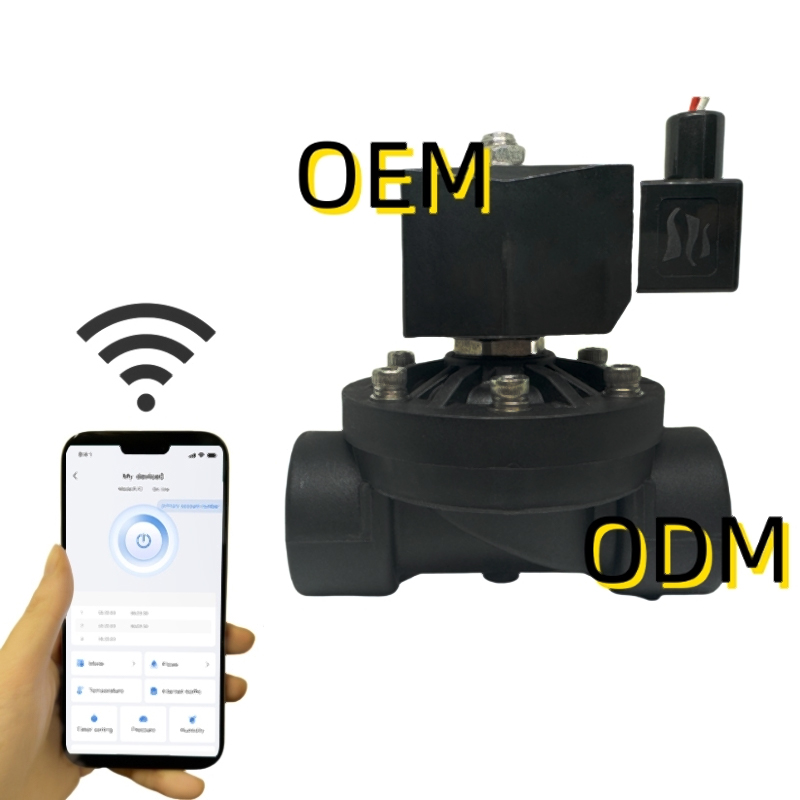
Choose communication layers that fit deployment constraints: BLE for commissioning and local control, Wi-Fi/4G for high-throughput telemetry, and LoRa for sparse remote sites. The app should support OTA firmware, parameter groups for bulk updates, and edge-enforced presets that the valve enforces locally during network outages to maintain safe operation.
Materials, sealing and media compatibility
Humidity-related applications can expose valve internals to corrosive fertilizers, biocides, or saline mists. Select corrosion-resistant internals and compatible elastomers rated for expected chemical exposure and temperature ranges. Compact designs reduce dead volume and allow retrofitting into existing piping while maintaining seal accessibility for periodic maintenance.
Diagnostics and maintenance workflows
Valves should report concise diagnostics: humidity trend deviation, valve position history, coil current signature, and battery health. The app translates telemetry into prioritized maintenance actions—calibration, filter cleaning, or actuator inspection—reducing time-to-repair and preventing avoidable crop or comfort loss.
| Telemetry item |
Why it matters |
Actionable threshold |
| Sensor divergence |
Detect failed or contaminated sensors |
Alert if >5% RH across 10 min |
| Coil current anomaly |
Indicates sticking or mechanical wear |
Alert on sustained >20% deviation |
| Battery voltage |
Prevents unexpected downtime in remote installations |
Warn at 20% capacity remaining |
Deployment examples and tailored strategies
In smart greenhouses, integrate App Humidity Control Solenoid Valves with plant-stage profiles: tighter control during propagation, relaxed ranges during vegetative growth to reduce fungal risk. In commercial HVAC, use coordinated valve scheduling tied to occupancy sensors to minimize latent load and energy use. Remote agricultural sites benefit from low-power sampling and LoRa-backed alarms that deliver concise fault packets for fast field triage.
When hardware, firmware and app are designed together, App Humidity Control Solenoid Valves become an operational asset rather than a field annoyance—reducing cycling, lowering maintenance cost, and delivering stable environmental conditions across diverse applications.



 English
English Español
Español